Last updated on August 26, 2025
Have you put your heart and soul into creating your site? This is an important step, but it's only the beginning. To be visible on Google, your pages still need to be properly indexed. In concrete terms, this means they must be registered in the search engine's database. So, how can you check if everything is working? A quick glance with the "site:" command, a visit to Google Search Console, or a few specialized tools is all you need. And if a page is missing? Don't panic: there are solutions to speed up the indexing of your website and optimize its visibility. Follow the guide!
What is website indexing?
Search engines like Google send their robots (crawlers : Googlebot, Bingbot…) to crawl your pages. If they are deemed relevant, they join the engine's index and may appear in search results. Otherwise? They remain invisible, as if they did not exist.
Good to know Being indexed doesn't mean being visible and well-ranked! Your page could end up relegated to the depths of Google, or worse, missing from competitive queries. Positioning depends on hundreds of SEO criteria, including:
- The keywords well chosen: they must correspond precisely to the search intention of Internet users.
- There quality and the relevance content.
- Optimization Technical SEO (loading time, HTML markup, structure…).
- L'site authority and the author (the famous signals EEAT : Expertise, Experience, Authority, Reliability).
- THE backlinks (inbound links): the more you are recommended by other quality sites, the better!
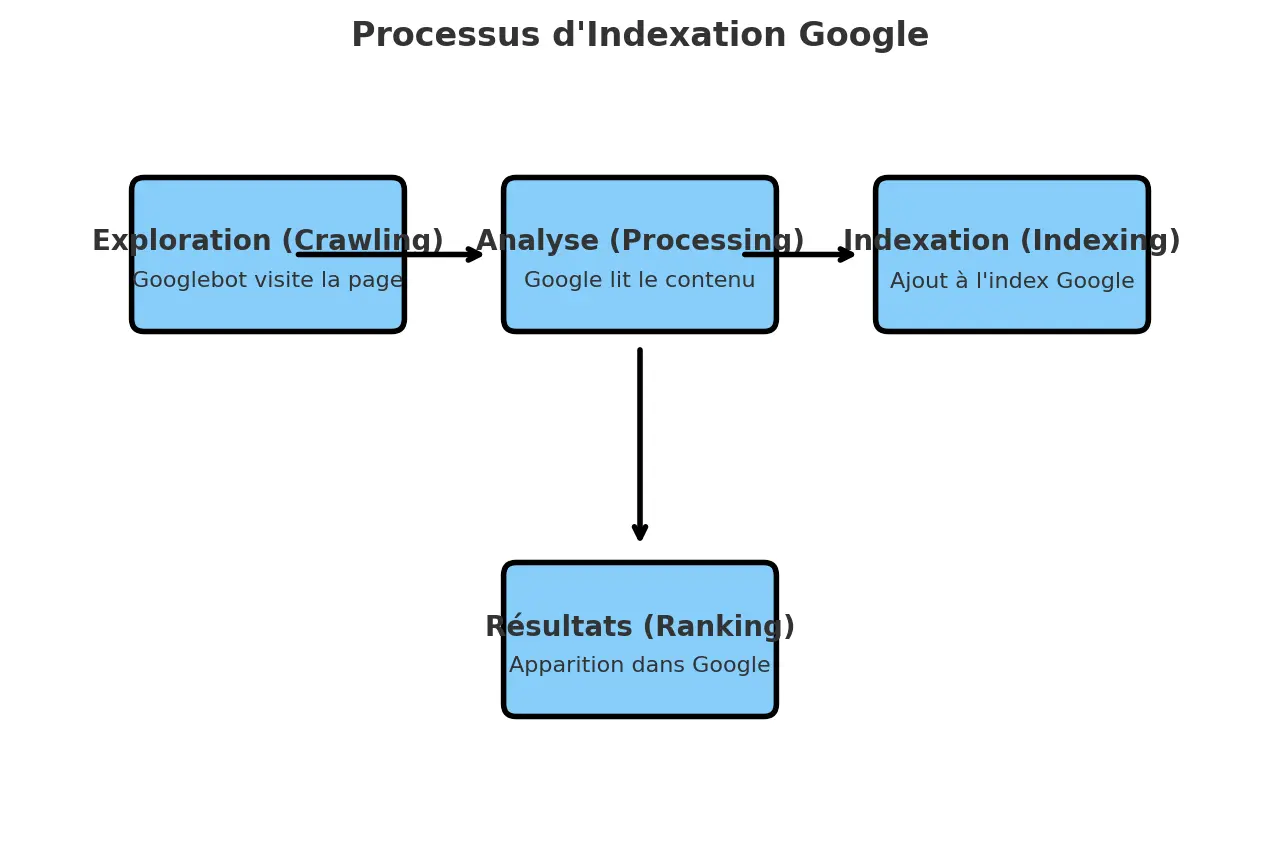
Why is website indexing important?
For natural referencing (SEO)
Without indexing, no visibility, no organic traffic: your site risks remaining a masterpiece... that no one sees. This is why'indexing is the gateway to SEO.
For user experience (UX)
Indexing a website is not just about pleasing the robots, it is also (and above all) about being there when your target audience is looking for you. Whether on mobile or desktop, your content must be easily accessible and perfectly meet the expectations of your audience. So, a well-indexed page is a page that can be found at the right time, by the right person. And that's the key to a good user experience!
What are the methods to check the indexing of a website?
1. The “site:” command: a quick look at your indexed pages
Simple, fast and accessible to everyone: this method allows you to see at a glance whether Google knows (or ignores) your site.
How to do it:
- Go to Google.
- Type in the search bar site: sitename.com
- Press “Enter”.
For example : for ouiscribe, enter: site:ouiscribe.com
What you'll see: A list of pages from your site that are in Google's index.
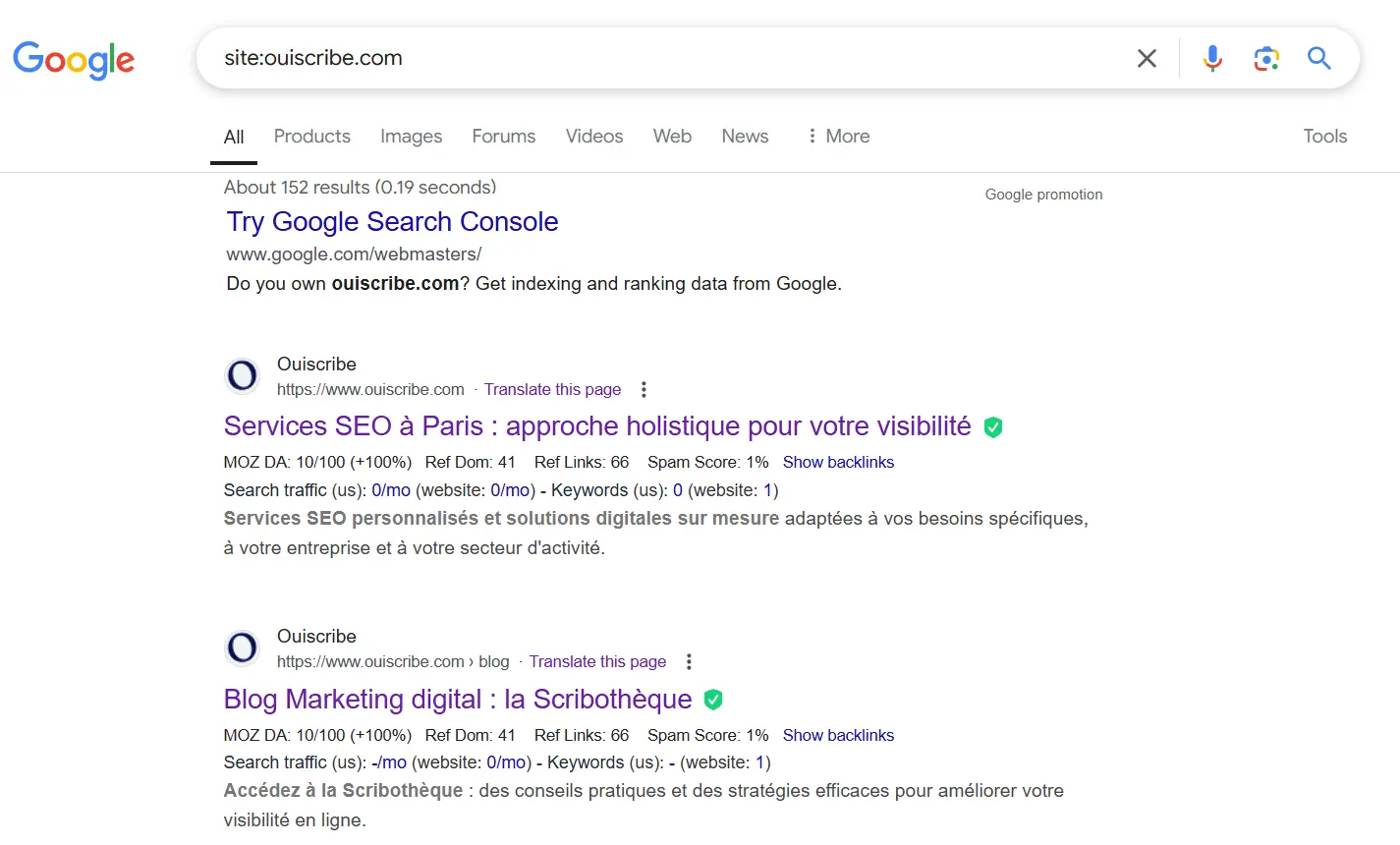
❌ No pages are displayed? Don't panic... or almost. This means your site isn't indexed. Google may not have had a good look around yet, but rest assured: there are ways to roll out the red carpet!
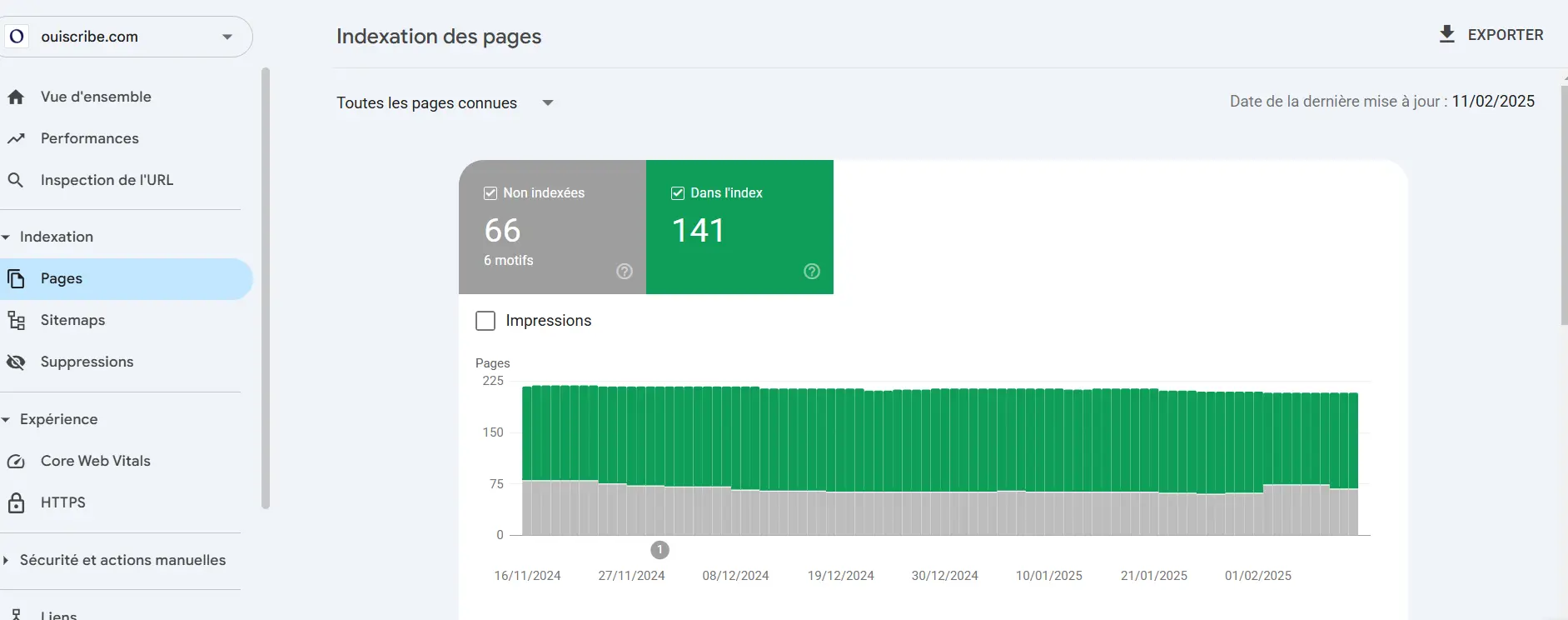
2. Google Search Console: Your Dashboard for Indexing
Google Search Console is the essential tool for monitoring and analyzing your website's indexing in detail.
How to check a page or the entire site:
- Log in to your Google Search Console account.
- Select your site from the list of properties.
- Go to the tab "Pages" to see the general status of indexing.
- For a specific page, use the option "URL Inspection" and enter the relevant URL.
Possible results:
- Pages in the index: Perfect, your content is well taken into account!
- Unindexed pages: It's time to dig deeper... This could be due to several reasons: page not found (404 error), "noindex" tag, page blocked by the robots.txt file.
Good to know : some pages may be voluntarily excluded from the index (e.g. redirects, legal notices). Nothing to worry about if it's a strategic choice!
3. Specialized online tools
If you want to go further, some tools offer you an even more in-depth analysis of your website's indexing.
Some must-sees:
Screaming Frog : to crawl your entire site and identify indexing issues.
Ahrefs / SEMrush : to analyze the presence of your pages in search results and identify potential errors (redirects, 403, 503 errors, etc.).
These tools are particularly useful for detecting technical blockages invisible to the naked eye.
How to see and fix technical blockages?
Even with the best content in the world, if Google can't crawl your pages, they'll remain invisible. Sometimes, small technical details can block indexing without you realizing it. Here are the main points to check to avoid unpleasant surprises:
1. The robots.txt file
THE robots.txt file acts as a gatekeeper at the entrance to your site. It can contain directives that prevent Google from crawling certain pages… sometimes by mistake. Check that Important URLs are not blocked involuntarily.
Where to check?
- Go to yoursite.com/robots.txt and look for lines like Disallow: /your-page/.
- In Google Search Console, use the URL Inspection tool to see if a page is blocked by robots.txt.
2. “No index” meta tags
THE no index tags are direct instructions to Google: they ask it not to index a page. Useful for certain secondary pages (legal notices, internal pages, etc.), but a real problem if they are applied by mistake to strategic content.
How to check?
View the source code of a page and search <meta name= »robots » content= »noindex »>.
In Google Search Console, the URL Inspection tool will tell you if a page is blocked by this directive.
If the noindex directive is blocking an important page, remove it!
3. The sitemap.xml
THE XML sitemap is a kind of map of your site that guides Google in its exploration. If it is missing or poorly configured, certain pages may be missed.
Must do:
Check that your sitemap is correctly generated (yoursite.com/sitemap.xml). If you don't know how to find a website's sitemap, our guide will be useful to you.
Make sure it is submitted and up to date in Google Search Console > Sitemaps.
A well-designed sitemap allows Google to locate your new pages more quickly and improve their indexing.
4. Exploration errors
Mistakes like 404 (page not found) Or 503 (site temporarily inaccessible) may prevent Google from accessing your pages.
How to spot them?
- In Google Search Console, go to Pages > Not indexed to see the list of affected pages.
- Test your links with tools like Screaming Frog to spot broken pages.
Fix errors by redirecting deleted pages to a relevant URL (301) or repairing broken links.
In short, indexing a website is first and foremost about ensuring a technically sound website. A quick visit to Google Search Console regularly and a check of your robots.txt file, your noindex tags, and your sitemap.xml will save you a lot of hassle.
How to request indexing of a website by search engines?
Sometimes Google and other search engines take their time indexing your pages. Fortunately, you can give them a little help by submitting your URLs directly. Here's how to speed up the process!
Submit a URL to Google
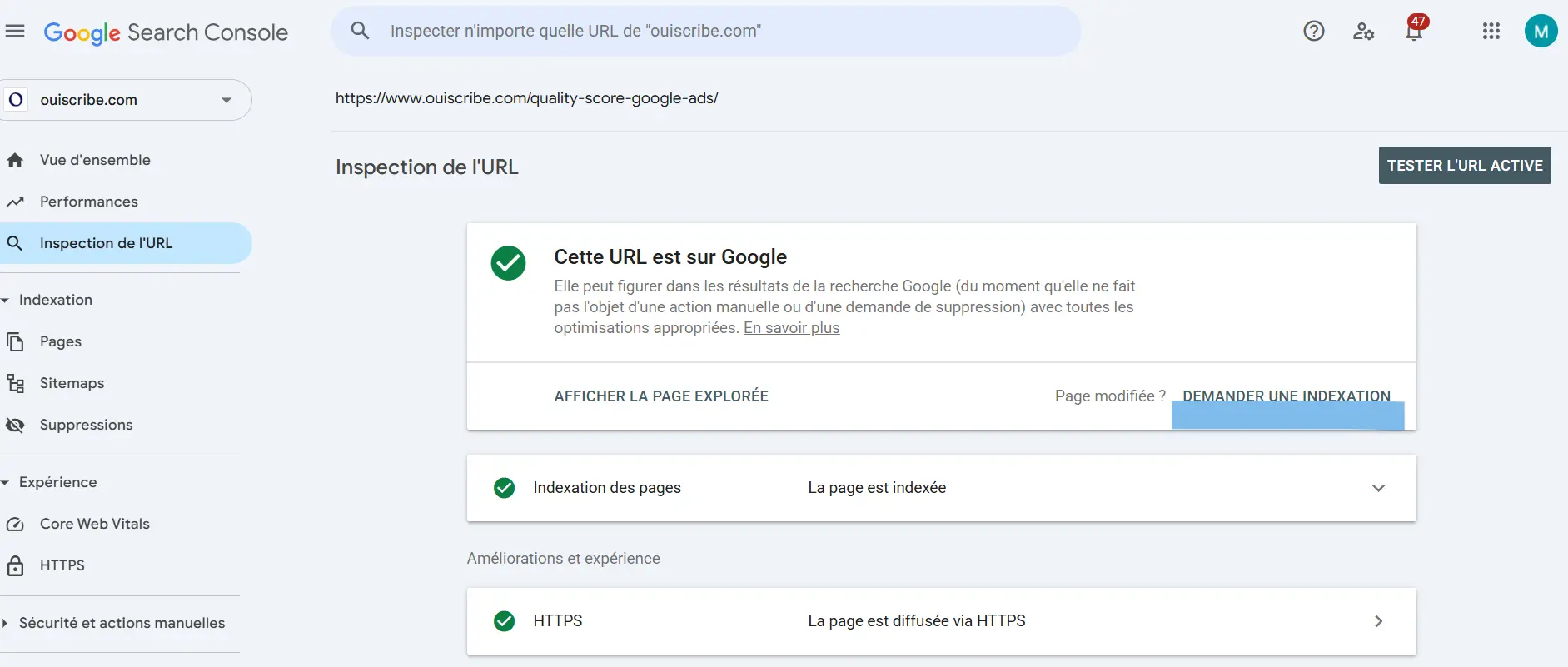
Google doesn't always find your new pages right away. To help it discover them faster, use the URL inspection tool In Google Search Console.
How to do it?
- Connect to Google Search Console.
- In the search bar at the top, paste the URL of the page to index.
- Click on “Request indexing”.
Namely : even after this request, indexing is not immediate. It may take a few hours to several days before Google considers your page. Be patient!
Submit a URL to Bing
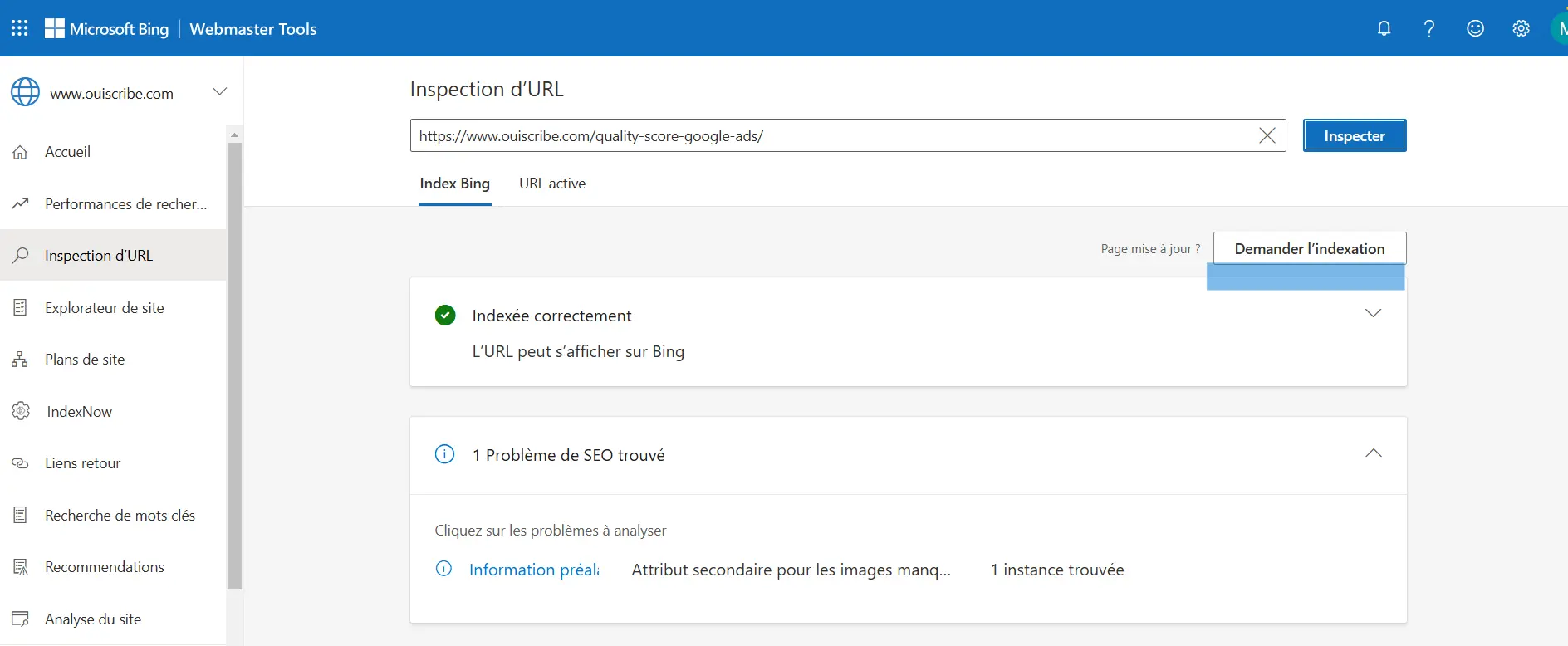
Bing is not to be overlooked, especially if you are targeting an international audience. Microsoft offers a similar tool via Bing Webmaster Tools.
How to do it?
- Go to Bing Webmaster Tools.
- Add your site if you haven't already.
- In the dashboard, select the “URL Inspection” option.
- Enter the URL of the page you want to index and click “Inspect”.
It's not indexed yet or you've made updates? No worries! Click on “Request indexing” to speed up the process and allow Bing to consider your page more quickly.
Submit a URL to Yandex
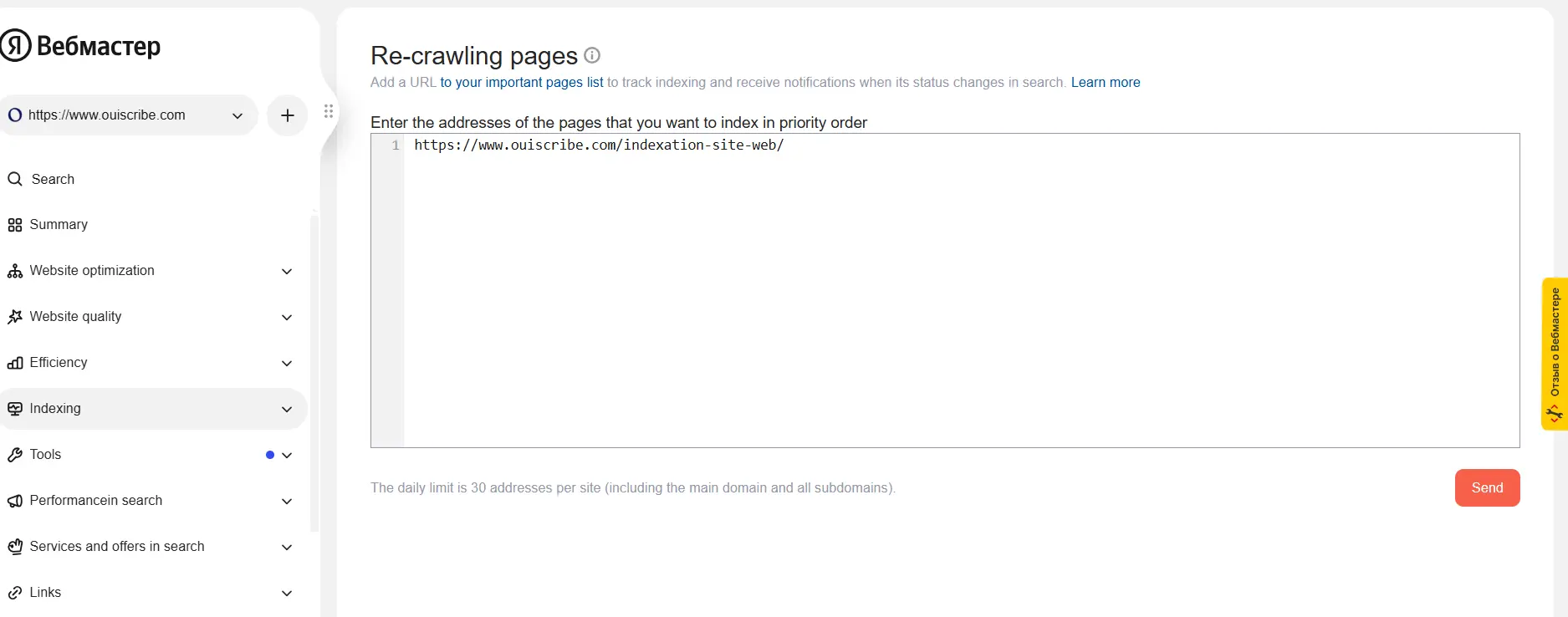
If your site targets Russian-speaking markets, also consider Yandex Webmaster Tools. Yandex works like Google and Bing, with an option to request indexing manually.
How to do it?
- Connect to Yandex Webmaster Tools.
- Switch the interface to English (if it is displayed in Russian, click on the language icon in the top right corner).
- Add your site if not already done.
- Go to “Indexing” > “Re-crawling pages”
- Enter the URL of the page you want to index, then click “Send”
Little reminder : Yandex has its own indexing criteria, including special attention to the structure and content of the site.
What about multilingual sites?
If your site exists in several languages, make sure that Google and other search engines understand which version to display depending on the user's language and location.
➡️ The solution: the hreflang tags
Example of an hreflang tag for a site in French and English:
<link rel= »alternate » hreflang= »fr » href= »https://example.com/fr/ »>
<link rel= »alternate » hreflang= »en » href= »https://example.com/en/ »>
These tags tell the engines which language version of a page displayed according to the user.
When properly configured, these tags prevent Google from considering your pages as duplicates and improve their international indexing.
How to create indexable content?
Having a well-designed website is great. But having content that Google can easily understand and index is essential! Good indexable content relies on: four essential pillars : meet the search intent, be well structured, technically optimized and quick to load:
- Respond to search intent : unique and relevant content that provides real value to users. No more duplicate content!
- Be well structured : use hierarchical titles (H1, H2, H3…) to facilitate reading and indexing of the website.
- Technical optimization : add descriptions alt to images to help Google interpret them and improve accessibility.
- Performance and speed : a site that loads in less than 3 seconds is favored by web robots… and appreciated by visitors!
Test your site with PageSpeed Insights to identify possible improvements.
Finally, choose good accommodation and avoid them useless scripts.
SEO Tip: Boost Your Visibility with Microdata
If you really want to stand out from the crowd, consider integrate microdata (also called structured data) to enrich your results in search engines thanks to enriched results (rich snippets) in the SERPs.
Why? Because Google loves to show enhanced results with reviews, prices, events, recipes… that catch the eye of Internet users! Some examples of useful structured data:
- Customer reviews : number of stars, comments.
- Products : prices, availability, promotions.
- Events : date, time, place.
- Recipes : cooking time, ingredients, steps.
- Items : title, author, publication date, summary.
Result: your page appears more attractive in search results, thus increasing your click-through rate And your visibility.
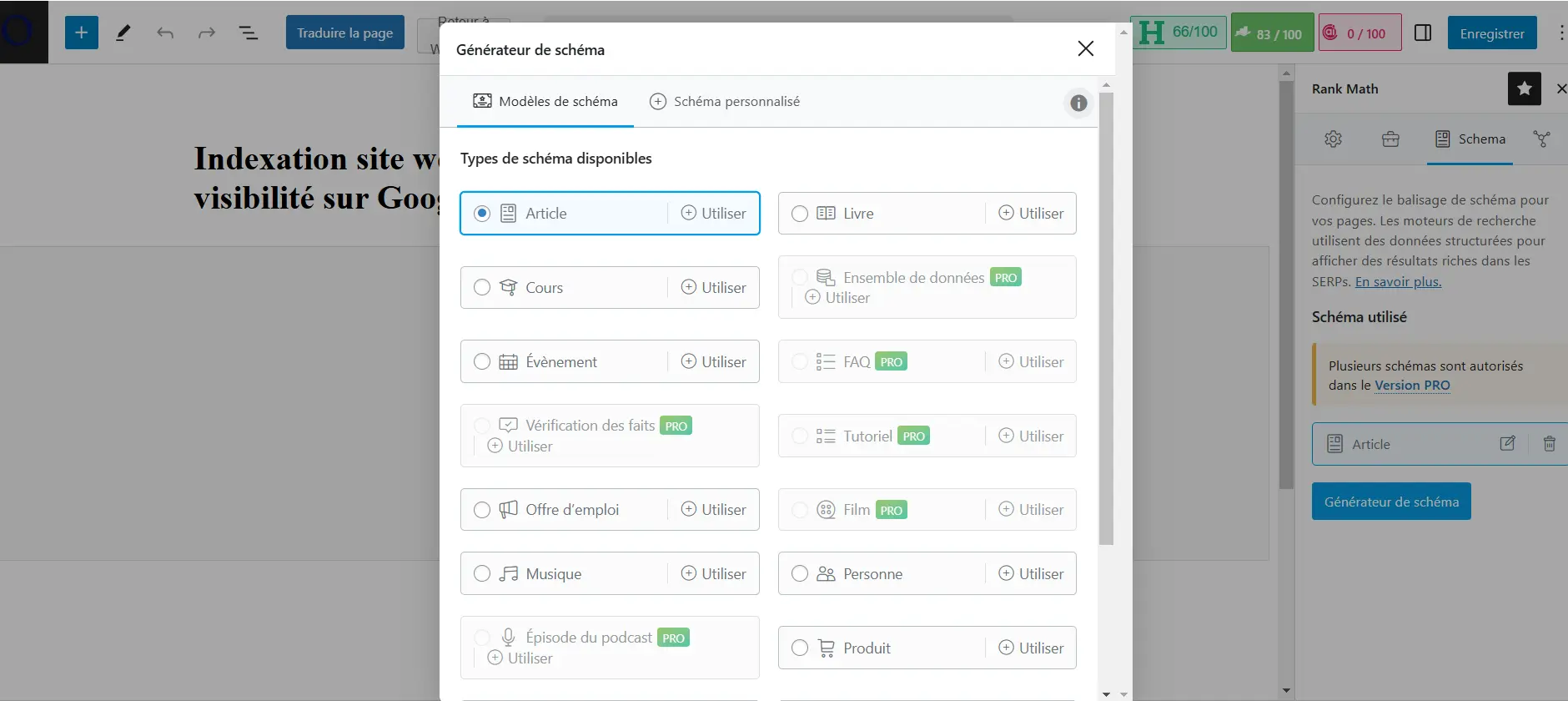
How to integrate them?
- Manual method: Add the JSON-LD code directly to your site.
- Simplified method: use a plugin! If your site runs on WordPress, extensions like Yoast SEO, Rank Math or Schema Pro make it easy to add these tags without touching the code.
What are the best practices for optimal indexing?
To ensure Google finds, indexes, and ranks your pages well, adopt these key best practices.
Update your content regularly
Google loves it content fresh and relevantA page left abandoned risks losing visibility, so don't hesitate to update it (every 6 months for example), enrich your articles and avoid any duplicate content.
Submit an XML sitemap
A XML sitemap, it's like a GPS for search engines: it tells them the structure of your site and makes it easier for them to explore.
Optimize your site's speed and security
Google favors sites fast and secureA website that loads quickly improves the user experience and boosts your SEO.
✔ To optimize:
- Reduce image size and use WebP format (use the Squoosh tool, for example).
- Enable caching and Gzip compression.
- Upgrade your site to HTTPS, an essential step : Google favors secure sites.
Need a hand? If you're using WordPress, plugins like WP Rocket or LiteSpeed Cache can help you improve your site speed in just a few clicks.
Create a strategic internal network
A good one internal mesh helps Google crawl your site and also directs your visitors to other relevant content.
Best practices :
- Connect your pages together with links consistent and natural.
- Use explicit link anchors (avoid the uninformative “click here”).
- Prioritize links to your strategic pages (business pages, services, key content) to strengthen their SEO weight.
Share your content on social networks
Even though Google does not directly take into account the social shares, strong visibility on Facebook, LinkedIn, Twitter (X), etc. can bring more traffic and signal to search engines that your content is interesting.
Trick : Consider integrating sharing buttons to encourage your visitors to share your articles!
Monitor your backlinks
THE backlinks (inbound links from other sites) are a strong signal for Google: the more links you get from quality, the more authority your site gains.
So how do you get good backlinks?
- Create content of value which naturally encourages sharing.
- Partner with sites in your industry.
Monitor your links with Ahrefs, Majestic or Google Search Console to spot potentially toxic ones. Disavow them only if necessary, as most of the time Google automatically ignores them.
What to remember
Website indexing is the foundation of your online presence. Without it, there's no visibility or traffic.
To ensure optimal SEO:
- Regularly check the indexing status of your pages using suitable tools.
- Fix technical blockages as soon as they appear.
- Create structured and relevant content designed for both search engines and users.
And if all this makes you feel like you're speaking another language, don't stress: Noèsna supports you with simplicity and expertise.
- How to do Pinterest keyword research? - October 21, 2025
- Website indexing: how to check and optimize your visibility on Google? - June 10, 2025
- SEO Redirection Plan: Instructions and Tips - June 10, 2025
